lumbosacral compression test osteopathic|omt sacrum flexion test : consultant Objectives. Discuss physiological changes of pregnancy. Review evidence related to pregnancy and OMT. Review common presentations and chief complaints of prenatal issues. Introduce .
Resultado da Publishing years: 1934-1944. 1952-present. Issues: 390. -. Format: Le journal de Mickey (post war series / first issue in June 1952 and still running) is a .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 18 de fev. de 2024 · Parece que el vídeo es falso xd cuando la persona grava como quedo . Citar. U. Un rangdom Anonimo. Miron Anonimo. 12 Ene 2024 #47 vash9f dijo: Ver el archivo adjunto 363119. . Portal; RSS; Community platform by XenForo .
Spring Test 1. Find sacral base 2. Place heel of hand over Lumbosacral junction 3. Spring in an Anterior motion 4. Results: a. Positive test = If there is NO springing allowed = Non-neutral condition (AKA Backward torsion ) b. Negative test = If there is springing allowed = Neutral . Diagnose the side of restriction with the ASIS compression test. Sit facing the patient on the side of the SI restriction. Contact under the pelvis at the SI joint with the .Chapter Ancillary Content: Textbook Materials. Chapter 01: Introduction to Osteopathic Diagnosis and Treatment. Chapter 03: Lower Extremity Diagnosis and Treatment. Video 3-24: .
lab scope compression test
Spring test (lumbosacral spring test) Function: assesses between physiologic and non-physiologic dysfunction; Position: prone; Procedure. Place hypothenar eminence on the lumbosacral junction. Apply a downward .If the test is positive (worsened asymmetry of the bases), this indicates a sacral extension dysfunction or a posterior sacral torsion. Sacral shears encompass bilateral and unilateral flexion and extension dysfunctions of the sacrum.Objectives. Discuss physiological changes of pregnancy. Review evidence related to pregnancy and OMT. Review common presentations and chief complaints of prenatal issues. Introduce . Used to determine if a sacral diagnosis is flexed or extended With the patient prone, the examiner monitors the sacral sulci while instructing the patient to extend by “getting .
Proper identification allows for the osteopathic technique's effective execution. The tests that can determine laterality are the standing flexion and ASIS compression tests. .
test. Anterior Superior Iliac Spines are compared for anterior-inferior position or posterior-superior position. One side may be rotated anterior & inferior, while the other side is the opposite. If you . The most common motion test was ASIS compression (68%), followed by OCF (61%), the standing flexion test (54%), and sacral springing (46%) [P < .0001, (Figure 4)]. The one-legged stork/Gillet test (12%), thigh .further testing is indicated. If one test is positive, the compression test is applied and if positive, a painful SIJ is likely and no further testing is required. If compression is not painful the sacral thrust test is applied. If this is painful, SIJ pathology is likely, whereas if it is not painful, SIJ pain is
Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Sacroiliac Joint (SIJ) Compression Test or “Approximation Test” is a pain provocation test which stresses the SIJ structures, in particular, the posterior SIJ ligament, to attempt to replicate patient’s .(ASIS) compression test. Also called ASIS ilial compression test. (1) A test for lateralization of somatic dysfunction of the sacrum, innominate, or pubic symphysis. (2) Application of a force through the ASIS into one of the pelvic axes to assess the mechanics of the pelvis. See also sacral motion, axis of. (Fig. 4) Lumbosacral radiculopathy is characterized by pain resulting from compression or irritation of nerve roots in the lumbosacral region of the spine, along with numbness, weakness, and reflex changes. . During physical examination, various maneuvers can aid clinicians in diagnosing lumbosacral radiculopathy. The Lasègue test, or straight leg .the standing flexion test, 4-9 seated flexion test,4-9 sacral springing,1,4-9 pelvic rocking,1,4,5,8 ASIS Compression Test,4,7.8 sacral motion with respiration and cranial rhythmic impulse,5,6,8 one-legged Stork test / Gillet Test,4,6 Trendelenburg Test,4,8 lumbosacral spring test, 6,8 backward bending test,6,8 standing trunk sidebending,6
Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Spurling's test (also known as Maximal Cervical Compression Test and Foraminal Compression Test) is used during a musculoskeletal assessment of the cervical spine when looking for cervical nerve root compression causing Cervical Radiculopathy.. Technique [edit | edit source]. There are different ways described in the literature to perform .
Newer studies show that vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty often relieve pain from compression fractures for at least a year. A compression fracture is a sign of weakened bones. People who have one compression fracture have a higher risk of more fractures in the future. That's why it's important to also diagnose and treat the cause of the bone .The L5-S1 spinal motion segment, also called the lumbosacral joint, is the transition region between the lumbar spine and sacral spine in the lower back. In this region, the curvature of the spine changes from lumbar lordosis (forward curve) to sacral kyphosis (backward curve). L5-S1 helps transfer loads from the spine into the pelvis and legs. The lumbosacral (LS) plexus is a network of nerves formed by the anterior rami of the lumbar and sacral spinal cord. LS plexopathy is an injury to the nerves in the lumbar and/or sacral plexus. LS plexopathy is not an uncommon condition but can be difficult to diagnose and manage.[1] However, it is far less common than brachial plexopathy. Patients with LS .
General. The lumbar spine follows Fryette laws of spinal motion.See “ Fryette laws ” in “ General osteopathic principles.” Motions: flexion and extension (main motions), sidebending, and rotation The greatest range of motion in the lumbar spine is flexion.; Lumbosacral angle (Ferguson angle) Refers to the intersection of a horizontal line that runs .
suture compression of the viscerocranium and neurocra - nium. Data concerning the presence of intraosseous lesions of the cranial and sacral bones were also col-lected on the form. Osteopathic structural examinations were performed twice weekly, on Tuesdays and Fridays, with the new-born lying supine or prone in an open crib or an incu-bator.The first one concerned the results of lumbar compression test and of Lasègue and inverted Lasègue tests as exclusion criteria before the application of the manipulative protocol (HVLAM or SM). Even though our participants were all considered as asymptomatic, the different osteopathic tests used here may induce unexpected modifications of the .
quantification of lumbar lordosis typically determined by measuring the angle between the superior surface of the second lumbar vertebra and the inferior surface of the fifth lumbar vertebra; best measured from a standing lateral x-ray film. (Fig. 1) lumbosacral a., represents the angle of the lumbosacral junction as measured by Lumbar extension test: This test involves asking the patient to lean back while observing the reactions. The pain triggered during this extension often indicates irritation of the posterior facets, due to the compression exerted on the joints. Lateral rotation test: This test assesses pain during trunk rotation. The patient is asked to rotate . Piriformis syndrome is a neuromuscular condition characterized by hip and buttock pain. This syndrome is often overlooked in clinical settings because its presentation may be similar to that of lumbar radiculopathy, . Lumbosacral radiculopathy refers to a pain syndrome characterized by the compression or irritation of nerve roots in the lumbosacral region of the spine. . During physical examination, various maneuvers can aid clinicians in diagnosing lumbosacral radiculopathy. The Lasègue test, or straight leg test, involves passively raising one leg into .
8 American Association of Colleges of Osteopathic Medicine asymmetry barrier (motion barrier): elastic b. B backward bending: Opposite of forward bending. See extension. backward bending test: 1. This test discriminates between forward and backward sacral torsion/rotation. 2. This test discriminates between unilateral sacral flexion and .The highest rate of somatic dysfunction was found in the pelvic area of 63 newborns (40.7%). The sacroiliac joints were compressed unilaterally or bilaterally in 82 newborns (52.9%); the lumbosacral junction was restricted in 61 newborns (39.4%), and intraosseous lesions of the sacral bone were diagnosed in 57 newborns (36.8%).Sacroiliac (SI) joint dysfunction is a common cause of low back pain and accurate diagnosis can be challenging. A complete history and physical examination are critical in differentiating other . 01:20 -- ASIS Compression Test (Skeleton) 02:52 -- Sacral Landmarks (Skeleton) 09:21 -- Spring Test 11:13 -- Prone Pelvic Girdle Reset 11:30 -- Backward Bending Test, aka Sphinx Test 15:01 -- Ischial Reset 15:19 -- Seated Flexion Test 16:35 -- Seated Sacral Sulci Screening 19:31 -- Seated ILA Screening 22:10 -- MSU Stork Test 23:42 -- ASIS .
lab validator compression tester
Osteopathic manipulative medicine texts and educators advocate a range of approaches for physical assessment and treatment, but little is known about their use by osteopathic physicians in the United States. . The most common motion test was ASIS compression (68%), followed by OCF (61%), the standing flexion test (54%), and sacral .The best known clinical test is the straight-leg raising test The supine SLR is more sensitive than the seated SLR when it comes to the diagnosis of lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy. A pooled sensitivity for straight leg raising test was 0. 91 (95% CI 0.82-0.94), a pooled specificity 0.26 (95% CI 0.16-0.38) [7] .Pain in SI joint indicates pathology in the anterior portion of the SI joint; pain in the lumbar indicates lumbar involvement and anterior thigh paresthesia indicates femoral nerve stretch. Interpretation: This should be down bilaterally because at times people might not be flexible resulting in a false positive test.The sacral thrust test is a pain provocation test used to diagnose sacroiliac dysfunction. One single positive test does not have high diagnostic accuracy but a combination with other sacroiliac pain provocation tests gives valid evidence for sacroiliac dysfunction. The test is also known as: Sacral compression test; Downwards pressure test
Lumbar spinal stenosis is a clinical syndrome that affects more than 200,000 people in the United States annually. It is a common cause of chronic insidious low back pain, especially in older . Low back pain represents one of the most prevalent ailments in contemporary society. Statistics indicate that around 90% of individuals will encounter acute back pain at some point in their lives, with approximately 10% experiencing chronic low back pain.[1] The multifactorial nature of low back pain often makes its origins complex, with only about 15% of .
Fractures of lumbar vertebrae occur in the setting of either severe trauma or pathologic weakening of the bone, see image R L4 compression fracture.. Osteoporosis is the underlying cause of many lumbar fractures, especially in postmenopausal women.; Osteoporotic spinal fractures are unique in that they may occur without apparent trauma. Any injury that changes .
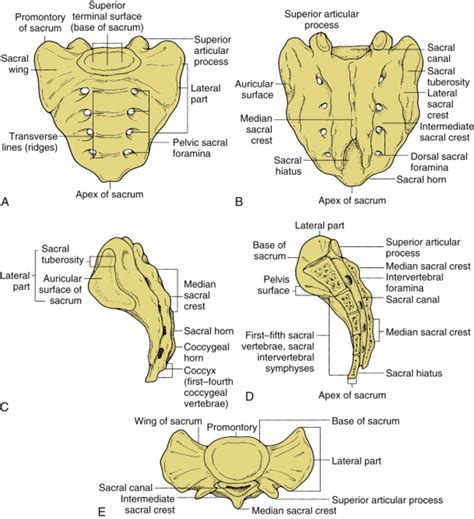
sacrum and sacral osteopathy diagram
labor to diagnose no start condition inclkuding compression test
sacrum and sacral osteopathy
sacral osteopathy positive test
WEB10 de nov. de 2023 · Estádio: Arena Barueri. Data: sábado, 11 de novembro. Horário: 21:00 (de Brasília) Árbitro: Paulo Cesar Zanovelli da Silva (FIFA/MG) VAR: Wagner Reway .
lumbosacral compression test osteopathic|omt sacrum flexion test